A number of new and recommended protocols have emerged to optimize data center Ethernet and support its server virtualization. The purpose of some of these protocols is to hope to achieve network virtualization by creating multiple virtual Ethernets that can share the same physical infrastructure. The sharing method is somewhat similar to multiple virtual machines sharing the same physical server.
Most of the protocols applicable to network virtualization basically use encapsulation and tunneling technology to create virtual network coverage. Among the most discussed protocols in the industry are VXLAN, NVGRE, STT and SPB MAC-in-MAC. SPB is already an IEEE standard, and among the various protocols that may become IETF standards, the most likely to become a standard is VXLAN.
Traditional network virtualization
One-to-many virtualization of network entities is not a new concept. The most common examples are VLAN and VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding).
VLAN can divide the network into 4094 broadcast domains at most, and assign a 12-bit VLAN ID for each broadcast domain in the Ethernet header. VLAN is a very convenient method to isolate different types of traffic in the same packet-switched LAN infrastructure.
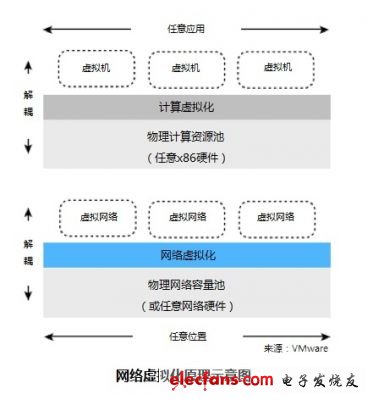
Data centers are heavily using server virtualization, and the limitation of the number of VLANs may cause problems, especially when a large number of tenants need to be supported and each tenant needs multiple VLANs. With the help of 802.1Q trunk links, VLANs can be expanded within the data center to support the mobility of VMs (virtual machines), but this will increase operating costs and complexity. Even in a data center based on a layer 2 server-to-server connection, a large number of VMs each have their own MAC address, which will also burden the forwarding table function of the layer 2 switch.
VRF is a type of layer 3 network virtualization, where the physical router supports multiple virtual router instances, each running its own routing protocol instance and maintaining its own forwarding table.
Unlike VLANs, VRF does not use tags in the header to specify a specific VRF for each packet. At each hop, an appropriate VRF is obtained based on the input interface and frame information. Another requirement is that each transit router in the end-to-end path through which a data packet passes needs to configure a VRF instance in order to be able to forward the data packet.
Leverage overlay network virtualization
Due to the shortcomings of the traditional VLAN or VRF model, many new technologies for creating virtual networks have begun to emerge. Most of them use encapsulation and tunneling technologies to build multiple virtual network topologies by covering them on the same physical network.
A virtual network can be a layer 2 or layer 3 network, and a physical network can be a layer 2, layer 3, or a combination of the two, depending on which overlay technology is used. Using overlay technology, the outer (encapsulated) header contains a 24-bit long field that carries a virtual network instance ID (VNID) to specifically designate a virtual network for packets to be forwarded.
The coverage of virtual networks can provide numerous benefits, including:
â— It can support virtually unlimited virtual networks; for example, a 24-bit header can create up to 16 million virtual networks.
â— Decoupling virtual network topology, service category (L2 or L3) and physical network addressing. This decoupling can avoid problems such as an excessively large MAC table on the physical switch.
â— Support the independence of virtual machine migration and physical network. If a VM wants to change its location or even migrate to a new subnet, the switch at the edge of coverage only needs to update its mapping table to reflect the new location of the VM. The new VM network is fully pre-configured at the edge of the network.
â— Manage the ability of multiple tenants to cover each other's IP address.
â— Support multi-path forwarding in the virtual network.
The main difference between the various overlay protocols is their encapsulation format and control plane functionality, which allows the entrance (encapsulation) device to map a frame to the appropriate exit (disassembly) device.
Dongguan Deli Plastic Co.,Ltd is a manufacturer specialized in the research, development ,plastic injection mould and making mass production with well-equipped facilities and strong technical force.
Our products are extensively used in household industry/electronic industry/automobile industry/building industry and other industries.
We have rich experience on one-stop solution, provide various services from new product design,prototype,mold making,mass production,assembly and logistics. The most important advantage is we have our own R&D team to help clients to turn ideas into actual parts. All of these engineers and designers have over 15 years experience in these plastic products fields.
We have a strict quality control system, an excellent management team and also a dedicated sales force, enable us to fulfill our commitment in high quality products and outstanding services.
If you are looking for a trustworthy supplier of customized items, please do not hesitate to contact us. We are always striving to establish a win-win partnership with customers from all over the world and help our partners to stay one step in front of your competitors.
usb Tower Fan,small Tower Fan,double tower fan
Guangdong Aiyimi Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.seventreasuresfan.com