1 Introduction
The frequency characteristic is the response characteristic of a system (or component) to a sinusoidal input signal of a different frequency. As shown in Figure 1, the system under test inputs a sinusoidal signal with an amplitude of Ar and an angular frequency of ω. If the system is linear, its steady-state output is also a sinusoidal signal, the frequency ω is constant, and the amplitude is Ac. The angular difference is φ. Changing ω gives you a series of input and output data. The ratio of the output to the input amplitude ratio A(ω)=Ac/Ar and ω is called the amplitude-frequency characteristic of the system, and usually takes 20 lg A(ω) as the logarithmic amplitude-frequency characteristic. The relationship between the output phase angle difference φ(ω) and ω is called the phase frequency characteristic of the system. The amplitude-frequency characteristic and the phase-frequency characteristic are collectively referred to as the frequency characteristic. The commonly used open-loop frequency characteristic of the system is the Bode diagram.

The frequency characteristics of a system can be determined by a frequency signature tester. The frequency characteristic tester is also called a frequency sweeper and is used to test the amplitude-frequency characteristics of the network under test. He can measure the resonant frequency, bandwidth, out-of-band attenuation, gain, etc. of the network under test, and is one of the commonly used devices in the electronics field. The analog frequency sweeper is more expensive, and can not directly obtain the phase frequency characteristics, and can not save the frequency characteristic map and the print frequency characteristic map, which brings a lot of inconvenience to the user. For this reason, the digital frequency characteristic tester is not counted. .
2 overall design
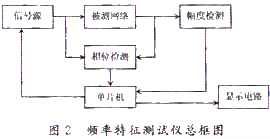
The single-chip microcomputer control signal source generates a standard sine wave and inputs it to the network under test; the output of the measured network is input into the amplitude detection circuit and the phase detection circuit respectively, and the peak and phase difference values ​​are sent to the single-chip microcomputer for processing; the result of the single-chip processing is provided on the one hand The LED is displayed in real time, and on the other hand, the memory is stored for the oscilloscope to display the amplitude and phase frequency curves. The overall frame is shown in Figure 2.
2.1 Design of frequency sweep signal source
The sweep signal generator is the core of the frequency characteristic tester. It provides a sinusoidal signal whose frequency required for the input of the measured network changes periodically over a certain range. The methods for generating the frequency sweep signal include a phase locked loop (PLL) and a preset prescaler, a monolithic integrated waveform generator, a dedicated frequency synthesizing device, and a direct digital frequency synthesizing (DDS) circuit. The system adopts single-chip control, and uses EDA technology to select the system programmable logic device ispCPLD chip to form a direct digital frequency synthesizer (DDS) to generate a scanning sine wave.
Direct Digital Frequency Synthesis (DDS) is a purely digital method. Because DDS has ultra-high frequency conversion time, extremely high frequency resolution and low phase noise, DDS devices can maintain phase continuity during frequency change and frequency modulation, so frequency, phase and amplitude modulation are easy to implement. DDS also has the outstanding advantages of programmable control. DDS is mainly composed of phase accumulator, sinusoidal ROM table and digital-to-analog converter. Its core is phase accumulator. It consists of a binary adder of N-bit length and an N-bit register sampled by clock fclk. Linear accumulation of frequency control words. When the phase increment is 1, and the word width of the accumulator is 32 bits, the output address corresponds to the phase resolution of the waveform as l/232. A sinusoidal function lookup table is stored in the sinusoidal ROM table, and different amplitude codes are output corresponding to different instantaneous phase codes. During operation, the control word is written into the DDS and converted into an instantaneous phase. Under the action of the external reference clock, the phase accumulator accumulates the phase step once per clock cycle, and the corresponding amplitude code is output to the digital-to-analog converter. (D/A), convert the digital quantity into analog quantity, and then smooth it through the low-pass filter to get the last desired signal. And the analog sine wave is compared with a threshold voltage to obtain a square wave clock signal of the same frequency, and the amplitude digital quantity of the discrete sample points of the desired sine wave is stored in the ROM, and then at a certain address interval ( The phase increment is read out, and an analog sinusoidal signal is formed by the D/A converter, and a better quality sinusoidal signal is obtained through the low-pass filter.
The frequency f0 of the signal generator output waveform is defined as:
Where fc is the crystal frequency, k is the division ratio, N is the number of phase accumulator bits, and M is the increment of the phase accumulator (step size).
In this design, fc=32.768 MHz, k=50, N=16, which can be obtained by substituting the above formula:
Thus, as long as the value of M is controlled, the frequency stepping requirement of 10 Hz can be accurately achieved. Here the clock frequency is:
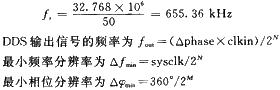
Where â–³phase is the frequency control word, sysclk is the system clock, clkin is the input reference clock frequency of DDS, N is the number of bits of the frequency register, and M is the number of bits of the phase offset register. The frequency control word â–³phase determines the frequency value of the output signal; the minimum frequency resolution is determined by the number of bits N of the frequency register, the larger N is, the higher the frequency resolution; the phase resolution is determined by the number of bits of the phase offset register, the amplitude The resolution is determined by the accuracy of the D/A converter. 
French Usb Power Strip,Desktop Power Strip,Long Power Strip,Usb C Power Strip
CIXI KYFEN ELECTRONICS CO.,LTD, , https://www.kyfengroup.com