In order to optimize the ECU communicating via the FelxRay bus, Audi calibrates it with XCP on FlexRay. One of Audi's needs is that AUTOSAR is compatible with the XCP embedded software modules inside the ECU. In response, Vector updated XCP's master and slave software to enable electronic development engineers to perform measurements and calibrations efficiently.
This article refers to the address: http://
In 2009, Audi will use the FlexRay bus to communicate on the next-generation sports luxury sedan. The FlexRay bus offers up to 10MBit/s of bandwidth compared to the CAN bus. Both the chassis and the driver assistance system are connected to this bus. This means that the Audi development engineer must parameterize thousands of parameters directly in the AUTOSAR FlexRay protocol stack. With XCP on FlexRay, it is possible to obtain measurements that are twice as large as CAN communication, while also enabling high-throughput data transmission.
XCP on FlexRay
The use of laboratory models to determine the parameters of the control algorithm is greatly limited. Although the functional algorithm is deterministic, like the feature map, the characteristic curve and some parameter values ​​must be optimized on the test bench and on the real car. Audi engineers adjusted their chassis and auxiliary systems in the ECU's calibration architecture and downloaded the parameter settings file into the ECU's memory.
In order to have a uniform interface throughout the development process, the measurement and calibration protocol standards must be uniform. In 2003, ASAM (Association for Standardization of Automation and Measuring Systems) defined a unified measurement and calibration protocol, the XCP protocol, which is based on the CCP protocol. The XCP communication topology is also the Master-Slave structure mode. As a slave, in order to be able to communicate, the ECU must integrate the XCP software module. The biggest advantage of the XCP protocol is that the transport layer and the protocol layer are independent. The protocol layer is the same whether it is CAN bus, FlexRay bus, Ethernet or SPI/SCI. In February 2006, ASAM released the 1.0 version of the XCP on FlexRay protocol.
In earlier CAN projects, the Audi development team used XCP and CANape for ECU measurement, calibration, and diagnostics (see Figure 1). Since 2005, CANape has supported the XCP on FlexRay interface. Audi requires the supplier XCP master to be CANape and the XCP on FlexRay protocol in the slave.
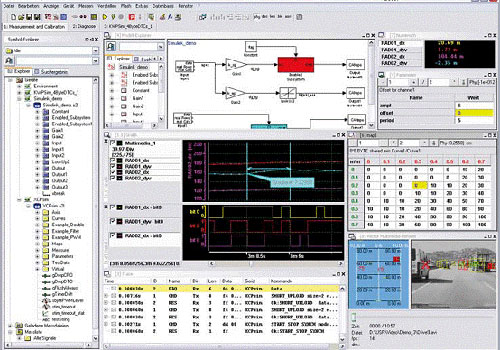
As the XCP on FlexRay master, CANape directly measures and calibrates a single ECU via the FlexRay bus
XCP integrated in the AUTOSAR module
Audi integrates XCP software modules into ECUs from different vendors. Even after the ECU calibration is over, the XCP software module is useful to use memory efficiently and minimize execution time. In addition, the XCP software module must be compatible with AUTOSAR, and XCP is compatible with AUTOSAR by using PDU router, Vector. When integrated, the GENy configuration tool and the network description file in FIBEX format can help configure the XCP protocol and the XCP transport layer.
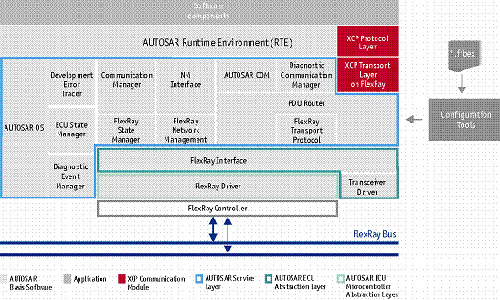
The XCP software module provided by Vector is compatible with AUTOSAR 3.0 architecture
Dynamic management of FlexRay bandwidth
Since the XCP on FlexRay software module must be compatible with AUTOSAR, this means that the PC supporting the master must also perform special tasks. During ECU calibration, FlexRay message exchanges are performed between the XCP master and the slave. These messages either contain Command Transfer Objects (CTOs) or contain Data Transfer Objects (DTO) or stimulus data. When the XCP object is transferred to the master (see Figure 3), the "XCP Transport Layer" transfers the data to the PDU router and goes to the "FlexRay Interface". Since it is compatible with AUTOSAR, these transmissions must be in accordance with the AUTOSAR PDU (Protocol Data Unit) format. Because the PDU comes from the XCP module, it is called an XCP-PDU. The FlexRay interface completes the received XCP-PDU by adding specific information in the form of PCI (Protocol Control Information) to form an L-PDU (Data Link Layer PDU), which is handed over to the FlexRay driver. Finally, the FlexRay controller transmits XCP data as a frame in a FlexRay slot.
It is sufficient to separately allocate two XCP slots to the ECU's control commands (CTOs); for DTOs, the XCP slots for each ECU are different.

Block diagram of data transmission via different software modules
To ensure that Audi engineers can efficiently transmit XCP data, bandwidth must be dynamically allocated while the ECUs are running. However, AUTOSAR does not allow the FlexRay driver to be reconfigured at runtime, so all XCP time slots are assigned to all ECUs when integrating the FlexRay driver; at the same time, when XCP-PDU/L-PDU/XCP is assigned in each slave, Gap (see Figure 3). Thus the FlexRay schedule for each ECU has a unique XCP time slot, and this time slot is available for each individual XCP buffer. In order to make the ECUs very flexible before each measurement, the XCP transport layer command "FLX_ASSIGN" can be used to change the allocation of XCP buffers for different L-PDUs (Figure 4). In software integration, the most important thing is to configure all the ECUs involved in communication with the largest XCP time slot, so that the XCP time slots of each ECU are consistent. Dynamic bandwidth management ensures a unique XCP time slot allocation across all Slaves. CANape can manipulate these tasks in the ECU description file A2L database, and the A2L description file provides information about the ECU buffer.
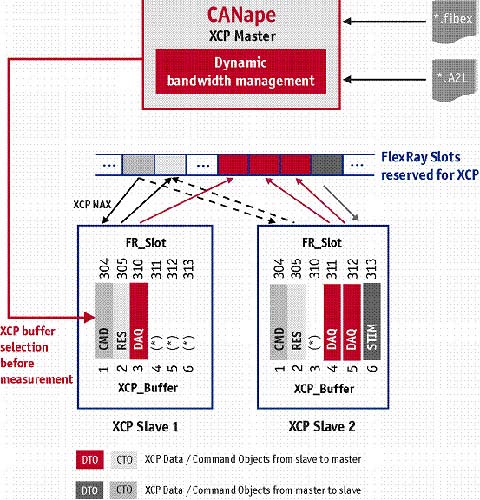
XCP objects are dynamically configured in dynamic segments before each measurement
XCP optimizes ECU internal data via FlexRay bus
CANape's dynamic bandwidth management function is just one of the CANape functions, which helps Audi to effectively calibrate the ECU. The other three functions are: the FlexRay bus can transmit up to 254 bytes of data, while the CAN bus can only transmit 8 bytes of data in each frame of the message; the "Short DownLoad" function can be in a single L-PDU. The address and content are encoded so that the master and slave exchange the memory area faster than CAN.
In addition, to measure each dynamic signal (Figure 5), the XCP can sample independently of the FlexRay cycle. CANape can use a function called "Multiple DAQlist Transmission Periods" to obtain pre-defined DAQlist measurement signals and their multiple timestamps (usually 5ms) in each FlexRay base period.
Ceramic Guides,Ceramic Eyelet Guide,Ceramic Eyelet Guides,Eramic Eyelet Guide
Yixing Guangming Special Ceramics Co.,Ltd , https://www.yxgmtc.com