Ion chromatography is used to analyze ammonia nitrogen in surface water, groundwater, drinking water sources, etc., and other cations can be detected simultaneously with methanesulfonic acid as mobile phase. The quantitative range of ammonia nitrogen is 0.04~15mg/l.
Ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) is a nutrient salt. Fish is sensitive to ammonia nitrogen in water, and high ammonia nitrogen levels can cause fish to die. The source of ammonia nitrogen in water is mainly the decomposition products of nitrogenous organic matter in domestic sewage by microorganisms, some industrial wastewater, such as coking wastewater and synthetic ammonia fertilizer plant wastewater, and farmland drainage. In addition, in an anaerobic environment, the nitrite present in the water can also be reduced to ammonia by the action of microorganisms. Determination of this form of nitrogen compounds in water helps to assess the contamination of water bodies.
The method for determination of ammonia nitrogen generally has Nessler colorimetric, gas phase molecular absorption, phenol-hypochlorous acid colorimetric, etc. The photometric method has a measurement range of 0.02-2 mg/l, and has many interference factors, and the operation is relatively cumbersome. A variety of reagents, including some toxic reagents, have problems with safe disposal of waste after measurement. Gas phase molecular absorption spectroscopy is the oxidation of ammonia and ammonium salts to nitrite to determine ammonia nitrogen, so the nitrite in the water sample needs to be calculated to be deducted, and the oxidant will also oxidize the organic amine in the water to nitrite. It also needs to be separated and removed in advance.
Ammonia nitrogen exists in the form of free ammonia (NH3) or ammonium salt (NH4+) in water. The composition ratio of the two depends mainly on the pH of the water. The ion chromatography is used, the mobile phase is acidic, and the ammonia nitrogen is completely converted into ammonium salt. Adjust the pH. For relatively clean water samples, such as groundwater and drinking water sources, the samples can be directly injected for easy operation. One injection can simultaneously detect other cations and improve the analysis efficiency. The method detection limit, recovery rate, precision and other indicators were investigated.
Experimental part
Main instruments and reagents
Ion Chromatograph:
Diane ion chromatograph
ICS-1500 with Dionex Ionpac CG 12A cation guard column (4×50mm), CS 12A anion separation column (4×250mm), CSRS 300 chemical suppressor (4mm), American Dion Company;Pipette: P10ml, Gilson, France;
Sodium, ammonia nitrogen, potassium standard solution, ammonia nitrogen standard samples are from the Institute of Standards and Research (IERM) of the Ministry of Environmental Protection, the standard solution mass concentration is 500mg / l, the ammonia nitrogen standard number is 200541;
The test water is ultrapure water (resistivity 18.25 MΩ / cm)
Chromatographic conditions
Isocratic elution with 10 mmol/l methanesulfonic acid, the eluent flow rate was 1.0 ml/min, the column temperature was maintained at 30 ° C, and the injection volume was 25 ul; the retention time was qualitative and the peak area was quantified. The sample was collected and stored in a clean polyethylene bottle. The sample was injected into the instrument after being applied to the 0.2 um filter of the needle.
Results and discussion
Working curve
The sodium ion, ammonia nitrogen and potassium ion standard stock solutions were diluted with water into a series of mixed standard solutions with concentrations of 0.10, 0.50, 1.00, 2.00, 5.00, 10.00, 15.00 mg/l, and different concentrations and corresponding peak areas were obtained by injection analysis. In response to the signal values, the chromatogram is shown in Figure 1. The three ions are better separated.
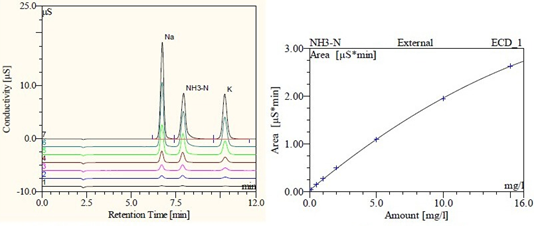
The ammonia nitrogen working curve is shown in Figure 2. The origin is not included in the fit. Sodium and potassium adopt Linear linear fitting standard curve, the linear correlation coefficient reaches 0.9999, and the absolute value of intercept is slightly less than 0.03. However, the linear fitting effect of ammonia nitrogen is not good, the linear correlation coefficient is only 0.992, and the curve equation is y= 0.1775x+0.0826. The Quadratic quadratic curve fitting method is used to obtain the working curve equation as y =-0.0041x2+0.2347x+0.0225, and the correlation coefficient is 0.9998. The correlation, slope and intercept are better than linear fitting, indicating that ammonia nitrogen is more suitable for this. The curve fitting method was used to calculate the ammonia nitrogen concentration from the working curve in subsequent experiments.
Precision and quantitative range
The standard solution of 10 mg/l in the working curve was repeatedly injected 9 times, the retention time of ammonia nitrogen was 7.920~7.933min, the RSD of retention time was 0.06%, the peak area was 1.92~2.01 μS•min, and the RSD of peak area was 1.24%. Thus, the precision of the method can be seen to be good.
Refer to EPA SW-846 and repeat the blank spike test 9 times according to the whole procedure. The scalar quantity is 3~5 times of the detection limit of the estimated method. Calculate the standard deviation of the measurement result, and use 98% confidence to check the t-distribution. The critical value table has t(8,0.02)=2.896, then MDL=2.896×SD, the quantitative method of the method is lower the RQL is 4 times MDL, and the detection limits of ammonia nitrogen and sodium potassium are calculated as shown in Table 1.
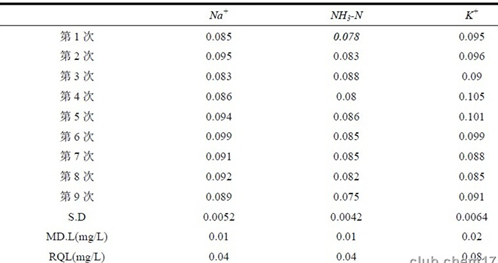
Ammonia nitrogen can be quantified between 0.04 and 15 mg/l. Among the national standards for water quality currently implemented, the standard water quality requirements for centralized drinking water surface water source standards [2] are the most stringent, and the limit for ammonia nitrogen is 0.15 mg/l. It can be seen from the test results that the lower limit of quantification of the method is lower than the water quality requirement of class I, so the lower limit of the method can meet the requirements of water quality monitoring.
Accuracy test
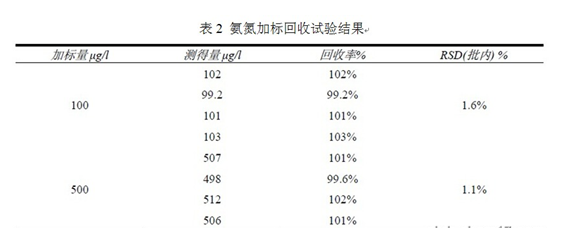
The concentration of ammonia nitrogen standard 200542 was 1.50 ± 0.07 mg / l, the standard solution was diluted 25 times as required, and the average parallel injection was 1.55 mg / l, within the quality control range. The spiked test samples were sampled with ammonia nitrogen, spiked twice, and each time the standard was measured 4 times. The measured value was subtracted from 1.50 as the measured value. The intra-assay standard deviation of ammonia nitrogen recovery rate and measured amount is shown in Table 2. From the test results, the ammonia nitrogen recovery rate is 99.2~103%, which is within 3 times RSD (within the batch) and meets the QA/QC requirements.
In addition, the same environmental water samples were detected by ion chromatography and Nessler's photometry [3], the sample concentrations were 0.95 mg / l and 0.90 mg / l, respectively, the standard deviation was 2.7%, less than 5% quality control requirements. Therefore, this method can be applied to the monitoring of water quality of relatively clean water samples such as surface water and groundwater. For the inclusion of organic wastewater, it can be considered after the pre-column treatment in series.
in conclusion
The detection limit of the method using ion chromatography is lower than the limit of ammonia nitrogen in the current national standard, which can meet the needs of monitoring work, and the precision of the method also meets the QA/QC requirements. Compared with the traditional measurement method, ion chromatography has the following advantages: simplifying the measurement process, reducing manual labor intensity; less solvent consumption, avoiding the use of some more toxic reagents, in line with the clean production concept; less water consumption, sensitivity High, wide measuring range.
CIXI LANGUANG PHOTOELECTRIC TECHNOLOGY CO..LTD , https://www.cxblueray.com