The Showa Aircraft Industry is developing a wireless power supply system that supplies large-capacity power for electric vehicles (EVs) and electric buses. This article will introduce a bus-centric wireless charging system that is powered while driving.
This article refers to the address: http://
At present, most electric vehicles (EVs) use contact chargers, but contact chargers have many inconveniences. Although the ordinary charger using the household power source is not too difficult to use, the quick charger has troubles in that the connector is large and heavy, and it is difficult to insert and remove. Previously, there were also products dedicated to improving operability, such as the use of the American SemaConnect automatic charger and the charger of the Honda robot arm, but these products will increase the cost.
In addition, contact chargers have safety and maintenance issues. In terms of safety, although there is generally no electric shock or leakage, users may have concerns when inserting connectors in the rain. In terms of maintenance, due to stains and wear on the contacts, frequent inspections and parts replacement are required.
In contrast, the contactless type eliminates the need for cable insertion and removal, which poses fewer safety issues during charging and reduces the cost of maintenance (Figure 1). Therefore, the Showa Aircraft Industry is currently developing a contactless charging system that can be safely charged even in the rain.
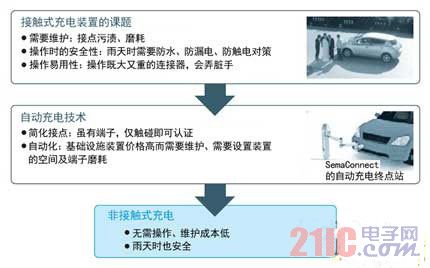
Figure 1: Non-contact charging is easy to use
Non-contact type requires no cable insertion and removal, in addition to excellent safety, it can also reduce maintenance costs.
There are three ways to use the car.
Lifting the wireless power supply system is generally mistaken for the work of the socket manufacturer, but we think it is one of the work of the charger manufacturer. The wireless power supply for automotive use does not transmit alternating current (AC) power through alternating current (AC) like a household outlet, but instead converts the AC to direct current (DC) and supplies it to a remote location (Figure 2).
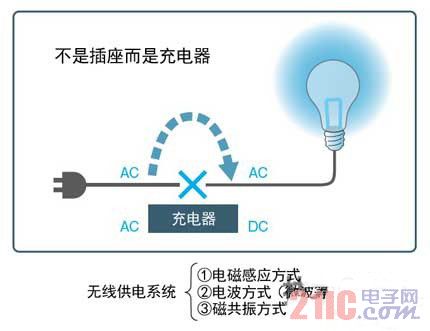
Figure 2: The wireless power supply system itself is the charger
A wireless power supply system can be said to be a charger that supplies power to a remote location.
There are three ways to provide wireless power for automotive applications: 1 electromagnetic induction, 2 radio, and 3 magnetic resonance (Table 1) Note 1). One of them utilizes the electromagnetic induction generated between the coils. It has existed since the 19th century and is a mature technology. It is characterized by high-efficiency transmission from small power to large power of 100 kW or more, and has been practically applied to various devices. Not only has it been promoted in terms of automotive use, but there are also many development examples in terms of light rail. The electromagnetic induction method has a stationary charging system in which the primary coil and the secondary coil are opposed to each other, and a mobile charging system equipped with a track for moving the power supply position of the primary coil (Fig. 3).
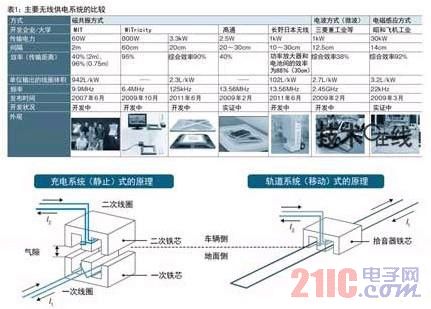
Figure 3: Electromagnetic induction can be roughly divided into static and mobile
There are static and extendable primary coils that are opposite each other between the coils as a moving type of power supply line.
Note 1) In addition, there is an electric field coupling method developed by Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
On the static side, Sanyo Electric has sold a wirelessly powered base and rechargeable battery kit for Nintendo's home console "Wii." On the mobile side, Bombardier's Transportation division in Canada has developed a wireless power supply system for electric trains that has been powered on the power line. It began to be put into practical use in Germany in November 2010.
The release of magnetic resonance methods continues
The radio wave mode of 2 is to receive radio waves and the like, and the rectifying circuit integrated with the antenna directly converts the radio waves into direct current. Long-distance large power transmission can be realized by reducing the beam of the electric wave. The Solar Power Generation Satellite (SPS) program, which supplies satellites from space to the ground, is currently being discussed between Japan and the United States.
In the automotive sector, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries has developed a microwave charging system with the assistance of the New Energy Industry Technology Development Agency (NEDO). Using the same 2.45 GHz radio wave generating device "magnetron" as the microwave oven, 1 kW of power can be transmitted to the underside of the vehicle floor via the "rectifying antenna". However, the current power transmission efficiency is not high.
In the magnetic resonance mode of 3, in June 2007, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) released a wireless power supply system that uses a resonance phenomenon between resonant circuits to transmit 60 W of power to a distance of 2 m. Since then, many companies and research institutions have been released.
Regarding the most interesting efficiency issue, the US WiTricity achieved an overall efficiency of 90% with an output power of 3.3 kW and a transmission distance of 20 cm. In addition, Nagano Japan Wireless achieved an efficiency of 88% between the power amplifier and the battery with an output of 1 kW and a transmission distance of 30 cm. Note 2).
Note 2) The "efficiency" of the wireless power supply system herein refers to the power transmission efficiency between the coils unless otherwise specified.
Power Noise Filter,3 Phase Filter,AC 3 Phase Filter,3 Phase RFI Filter
Jinan Filtemc Electronic Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.chinaemifilter.com