The sound absorbing material and the sound absorbing structure are roughly classified into the following categories: The first type is a porous sound absorbing material, including a fibrous material, a particulate material, and a foam material. These materials have the widest range of specifications and are the most widely used. The second type is a resonant sound absorbing structure, including a Helmholtz resonant sound absorber, a perforated plate resonant sound absorbing structure, a thin plate resonant sound absorbing structure, and a thin film resonant sound absorbing structure. The third category is a special sound absorbing structure, including a spatial sound absorber, a sound absorbing tip, and the like. There are also composite sound absorbing structures constructed from the first two categories.
The sound absorbing material and the sound absorbing structure are classified differently, and thus the sound absorbing principle is also different. This section focuses on the second type of resonant sound absorption structure, with the aim of providing some help in dealing with low frequency sound absorption. In particular, when there is a degeneracy of the room's normal mode in an acoustic small room, a solution is provided. In the process of dealing with low-frequency sound absorption in small rooms, especially in the process of handling simple mode degeneracy frequency sound absorption, the development of foreign technology in this technical field is worth learning. This is the emergence of low-frequency sound-absorbing modular components (a composite sound-absorbing structure), which makes the low-frequency room mode sound absorption products serialized, which greatly facilitates the problem of the acoustic surface of small room buildings.
Helmholtz resonance sound absorber
Resonance sound absorbers (commonly known as low-frequency traps) are usually used to deal with acoustic problems in small rooms. It is only unreasonable in the case where the size of the room is long, wide and high, and the room is not decent. Method. Even so, set the resonant absorber for the degenerate frequency. A resonant sound absorber of a certain frequency can only absorb room resonance waves near the frequency to reduce the acoustic staining phenomenon. Helmholtz resonators are typically used in small control rooms and studios. Large rooms will cost too much because they require too many Helmholtz resonators. A room with a volume of approximately 42.5 m3 or less has limited effectiveness due to the coupling of the resonators to each other to reduce their performance. The use of the device requires consideration that the use of these Helmholtz resonator devices (like almost all passive low frequency control devices) may occupy up to 10% of the room volume before the desired response is obtained.
A single Helmholtz Resona-toror is a hermetic container with a rigid interior that communicates with the outside air by means of a narrow, heterogeneous tube. Similar to a mass-spring combination with shock absorption, the loss of acoustic energy is provided internally. This is due to the use of acoustic attenuation due to the frictional damping of the air within the tube diameter as the sound waves enter the conduit.
When the frequency of the incident sound wave approaches the natural frequency f0 of the resonator, the air column of the duct produces a strong vibration, which is similar to the oscillation supported by the spring. In this process, heat energy is converted by consuming acoustic energy against frictional resistance. A significant sound absorption characteristic of Helmholtz resonant sound absorbers is that their sound absorption performance has a strong frequency selectivity. Only when the acoustic wave frequency is near the natural frequency fo of the resonator, has a large sound absorption coefficient, and the sound absorption performance of other frequencies deviating from the frequency fo starts to gradually decrease until the sound absorption is small.
The maximum sound absorption A of the Helmholtz resonance sound absorber fo frequency
The factors affecting the sound absorption of the Helmholtz resonance sound absorber are more complicated. It involves the Q value of the resonance sound absorber, the degree of damping, the sound absorption bandwidth, and even the placement position. The maximum sound absorption A is used as an estimate of the performance of the Helmholtz resonance sound absorber. If the frequency sound stain is severe, the number of resonance sound absorbers should be considered. As can be seen from the data in the table below, the maximum sound absorption of the device is reduced by a factor of 4 for each octave of the resonance frequency fo. This also provides a reference for us to consider the number of Helmholtz resonant sound absorbers at different frequencies.
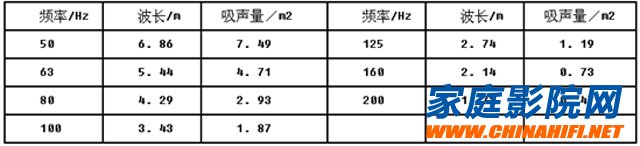
Helmholtz Resonance Sound Absorber Band
All of the above calculations were performed under rigid resonant cavity conditions. In some cases, thermodynamic effects can occur due to the internal filling of the resonant cavity. The insulator as the sound absorbing material absorbs thermal energy, so it has the effect of increasing the effective volume of the device. A change in the effective volume caused by the insulator. The change in its value gives a range of possible catheter lengths.
Home Theater Network () Tip:
1) Use rectangular wooden boxes carefully to make these resonant sound absorbers
In order to increase the rigidity to prevent the container from vibrating, it is strongly recommended to use a cylinder (tube) shape. However, if the flame-retardant glass wool fiber is internally filled, the vibration of the rectangular wooden box can be alleviated to some extent. Of course, the use of steel plates of sufficient thickness is another matter.
2) About the placement conditions of the device
The distance between the opening of the conduit and any object (such as a wall or floor) is at least twice the length of the inner tube, otherwise it will impede air circulation and reduce sound absorption efficiency.
3) Frequency conditions for device use
The response of the ear to the sound is related to the frequency. 2000~4000Hz is the most sensitive frequency range of the human ear to the sound. When the frequency is lower than 1000Hz, the sensitivity of the ear to the sound decreases with the frequency decreasing. Therefore, in the acoustic design of a small room, the low-frequency lower limit frequency of the speaker is also around 40 Hz, so the degenerate wave with a frequency lower than 40 Hz does not need to use a low-frequency resonator, that is, the Helmholtz resonator is usually used for a small room design in the frequency range above 40 Hz. . The table below requires a large sound pressure level at the low frequency to maintain the same loudness level. The data in the table is a comparison of five equal loudness curves below 50 Hz. Obviously, if the sound pressure level required to obtain the same loudness of 20 Hz is about 20 dB, the sound pressure level required to exceed 50 Hz; the sound pressure level required to exceed 100 Hz is about 30 dBo, which means that when using architectural acoustic treatment measures, it is also necessary to consider In-ear characteristics.
This can reduce the cost of acoustic decoration. Of course, higher music performance halls are required, the frequency of the source is lower, and the pursuit of a perfect acoustic environment is also necessary.
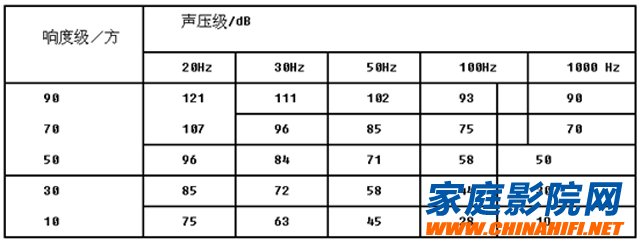
4) Quantity conditions for device use
The number of sound absorbers needs to be determined based on the degeneracy of the room's normal mode and the resonant frequency at which it is located. If you have the conditions to use the ETF meter, you can also determine the number of sound absorbers by increasing or decreasing the number of Helmholtz resonance absorbers to see the effect of measuring the "degenerate wave" resonance peak of the waterfall. As long as the resonance peak becomes gentle, the decay time is significantly shortened.
In summary, the Helmholtz Resonance Sound Absorber is a solution often used to deal with acoustic dyeing in small rooms.
Helmholtz Resonance Sound Absorber Construction Materials
When calculating all types of Helmholtz resonant sound absorbers, you need to consider how to build it.
Perforated plate resonance sound absorbing structure
1. Perforated plate resonance sound absorption structure
Sound absorption principle of perforated sound absorbing plate structure
A perforated plate sound absorbing structure is formed by wearing a circular hole of a certain density on a metal plate, a thin wood board, a cement board, and a gypsum board, and then providing a certain thickness of the air layer and a suitable porous sound absorbing material. At present, the medium-density fiber perforated plate sound absorbing products that have been mass-produced at the factory have size specifications of 2440×600×16, 1200×600×16, 600×600×16 and so on.
The mechanism of the sound absorption of the perforated plate is that when the sound wave enters the small hole, the air vibration in the cavity is excited. If the sound wave frequency and the gas layer and the appropriate porous sound absorbing material constitute the sound absorbing structure of the perforated plate. At present, the medium-density fiber perforated plate sound absorbing products that have been mass-produced at the factory have size specifications of 2440×600×16, 1200×600×16, 600×600×16 and so on.
The mechanism of sound absorption by the perforated plate is that when the sound wave enters the small hole, the air vibration in the cavity is excited, if the acoustic wave frequency and the resonant frequency of the structure (the perforated plate sound absorbing structure can be understood as many Helmholtz resonant sound absorbers) When the parallel connection is the same, the air in the cavity resonates. At this time, the air mass is violently rubbed by the wall of the hole and the porous sound absorbing material behind it, which is converted into heat loss. The consumption of sound energy causes sound absorption, thus showing The larger sound absorption coefficient; at other frequencies, the vibration of the air mass in the hole will be weakened (detuned), and the sound absorption coefficient is small. Therefore, the sound absorption frequency characteristics of the perforated plate structure exhibit obvious resonance characteristics.

The perforated plate structure has the largest sound absorption coefficient near the resonance frequency, and the farther away from the resonance peak, the smaller the sound absorption coefficient. The smaller the air movement resistance at the neck of the hole, the sharper the sound absorption frequency curve; otherwise, the flatter. In order to have a high sound absorption coefficient over a wide frequency range, a porous sound absorbing material may be placed behind the perforated plate to increase the resistance to air movement. In this way, the resonant frequency will move to the low frequency, but usually the offset will not exceed one octave range, and the sound absorption coefficient of the entire sound absorption frequency range will be significantly improved (the sound absorption coefficient can often be 0.6).
At present, a fireproof FC perforated sound absorbing plate sound absorbing material is commonly used, and the FC fiber cement pressure plate (calcium silicate board) is formed by using an organic and inorganic material such as silicon, calcium material and fiber through an advanced production process. High-tech products made of pressure, high temperature, high pressure steaming and special technical treatment are a new type of building sound absorbing panels that combine high strength, large format, light weight, waterproof and fireproof performance.
2. Micro-perforated plate sound absorbing structure
The apertures that are perforated with thin metal sheets are small (usually 0.8 mm) and are called microperforated sheets. When the hole is small, the ratio of the perimeter to the cross section is large, and the frictional resistance between the air and the neck wall of the hole is large, and the air viscosity loss in the micro hole is also large. Generally, the porous material is no longer laid behind the microperforated plate, and it has better sound absorption characteristics than the general perforated plate structure without the sound absorbing material. The outermost layer of microperforated plate has a perforation rate of 2%, and the inner perforated plate has a perforation rate of 1%, the two layers are separated by 80 mm, and the back space is 120 mm. It has a high sound absorption coefficient in the frequency range of 250~1000Hz. A major feature of this sound absorbing structure is its ability to withstand high temperatures, high humidity and no dust pollution.
Thin plate resonance sound absorbing structure
A thin plate with a certain elasticity such as plywood, fiberboard, plastic plate, gypsum board, FC board or metal plate is fixed on the wooden keel or light steel keel in large area so as to leave a certain depth of air layer (cavity) behind the board. The plate and air layer thus form a resonant sound absorbing structure.
When the sound wave is transmitted to the surface of the thin plate, the bending vibration of the thin plate is caused by the alternating action of the sound pressure. Due to the friction between the thin plate and the fixed fulcrum and the friction loss caused by the inside of the thin plate, the kinetic energy of the vibration is converted into heat energy, and the sound energy is attenuated, so that the energy of a part of the sound wave is consumed to achieve the purpose of sound absorption. It goes without saying that its sound absorption coefficient is greatest near the resonance frequency of the system.
Usually, the resonant frequency is selected in the range of (80~300 Hz) for low frequency sound absorption. Generally, the sound absorption coefficient near the resonance frequency can reach (0.2~0.5). In order to increase the sound absorption coefficient, a soft material such as felt, soft rubber or sponge strip is placed at the intersection of the plate and the keel, or some porous sound absorbing material (glass fiber cotton) is filled in the rear cavity. . There is also a semi-cylindrical shape of the sheet so that it simultaneously acts to increase the "diffusion" of the sound in all directions. These have some specifications in construction.
Large-scale plaster ceilings, overhead wooden floors, glass windows, and thin metal plate shades are also equivalent to thin-plate resonant sound-absorbing structures, which have a large absorption of low frequencies.
Sound absorption characteristics of several thin plate resonant sound absorbing structures
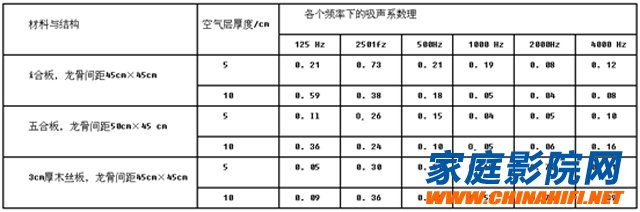
In summary, the resonant sound absorption structure mainly solves the sound absorption problem in the middle and low frequency bands. This knowledge will help us during the acoustic decoration of the room.
Low frequency sound absorption structure modular
In order to deal with the convenience of sound absorption in the small room mode, foreign acoustic designers have made the low frequency sound absorption structure into a sound absorption module of the same specification. Although they are the same size, the sound absorption frequency can be different.
Prototypes of modular sound absorbing components are given in the report "Modular Design of Low Frequency Sound Absorption Structures" published by the British BBC Research Department in the early 1990s. The side panels and the (bottom) rear panels must be plywood. Experiments have shown that alternative materials (such as 9mm thick MDF) on the side panels may produce a peak of sound absorption that we don't need.
The front panel is a hardboard and a mineral wool-filled sound absorbing member for sound absorption measurement in a reverberation chamber. A total of 28 module sound absorbing parts were used in the measurement. The total area given by the 28 modules (when the center distance is 600 mm) is approximately 10.1 ll12. The sound absorption coefficient below 125 Hz increases as the frequency decreases, increasing to a peak of 63 Hz and then falling to 50 Hz. The module achieves the desired sound absorption at low frequencies. Prototype module measurements also show a lower and wider sound absorption peak in the 200-500 Hz range.

Subsequently, RPG Diffusion Systems of the United States developed a series of low frequency sound absorbing components for acoustic processing of small room buildings. They are easy to install and use, and cover almost all the low-frequency sound-absorbing products in the small room. These low-frequency sound-absorbing products called Modex series include:
(1) Modex broadband sound absorption board. Dimensions: length 1.Sm, width Im, thickness 0.Im, processing 63-4000Hz sound absorption, wall-mounted installation.
(2) Modex sound absorbing panel. Dimensions: length 1.Sm, width Im, thickness 0. Im, processing sound absorption below 400Hz, wall mounted installation.
(3) Modex edge sound absorber. Dimensions: The height is 0.8m and the cross section is a right-angled trapezoid (the sides are respectively 0. 53m, 0.9m, 0.2m, 0.97m), and the sound absorption below 500Hz is processed, and the stacking is installed.
(4) Modex sound absorption module. Dimensions: length 0.6m, width 0. 6m, thickness 0.18 m, wall mount type 0 7 resonant frequency models available: 30Hz, 40Hz, 50Hz, 63Hz, 80Hz, 100Hz, 125 Hz ±1/3 oct.
(5) Modex angle type sound absorber. Dimensions: The height of 0.6m is a right-angled triangle (edge ​​lengths are o.6m, 0.42m, 0.42m, respectively). The two walls are installed at the corners of the corners or at the corners of the wall and ceiling. Three resonant frequency models are available: 40Hz, 63Hz, 80Hz ±1/3 oct.
It can be seen that the low-frequency sound absorption structure is modular, componentized, singular in size, convenient to install and use, and is a major trend in the development of contemporary low-frequency sound absorbing products.
ZGAR AZ BOX Vape
ZGAR electronic cigarette uses high-tech R&D, food grade disposable pod device and high-quality raw material. All package designs are Original IP. Our designer team is from Hong Kong. We have very high requirements for product quality, flavors taste and packaging design. The E-liquid is imported, materials are food grade, and assembly plant is medical-grade dust-free workshops.
Our products include disposable e-cigarettes, rechargeable e-cigarettes, rechargreable disposable vape pen, and various of flavors of cigarette cartridges. From 600puffs to 5000puffs, ZGAR bar Disposable offer high-tech R&D, E-cigarette improves battery capacity, We offer various of flavors and support customization. And printing designs can be customized. We have our own professional team and competitive quotations for any OEM or ODM works.
We supply OEM rechargeable disposable vape pen,OEM disposable electronic cigarette,ODM disposable vape pen,ODM disposable electronic cigarette,OEM/ODM vape pen e-cigarette,OEM/ODM atomizer device.

ZGAR AZ BOX Vape,ZGAR AZ BOX disposable electronic cigarette,ZGAR AZ BOX Vape vape pen atomizer , AZ BOX Device E-cig,AZ BOX disposable electronic cigarette
Zgar International (M) SDN BHD , https://www.oemvape-pen.com